Step-by-Step Guide
For aquaculture farms, wastewater treatment plants and municipal water systems, reliable real-time water quality data isn’t just beneficial—it’s mission-critical: preventing stock loss, ensuring regulatory compliance and mitigating public health risks. This guide outlines water quality sensor integration with the Bivocom TG452 Industrial Gateway. Via industry-standard RS485/Modbus RTU, it connects discrete sensors into a low-maintenance system, delivering accurate data to your monitoring platform—even in harsh conditions.

Prerequisites: What You’ll Need
Before you begin, gather your hardware and software.
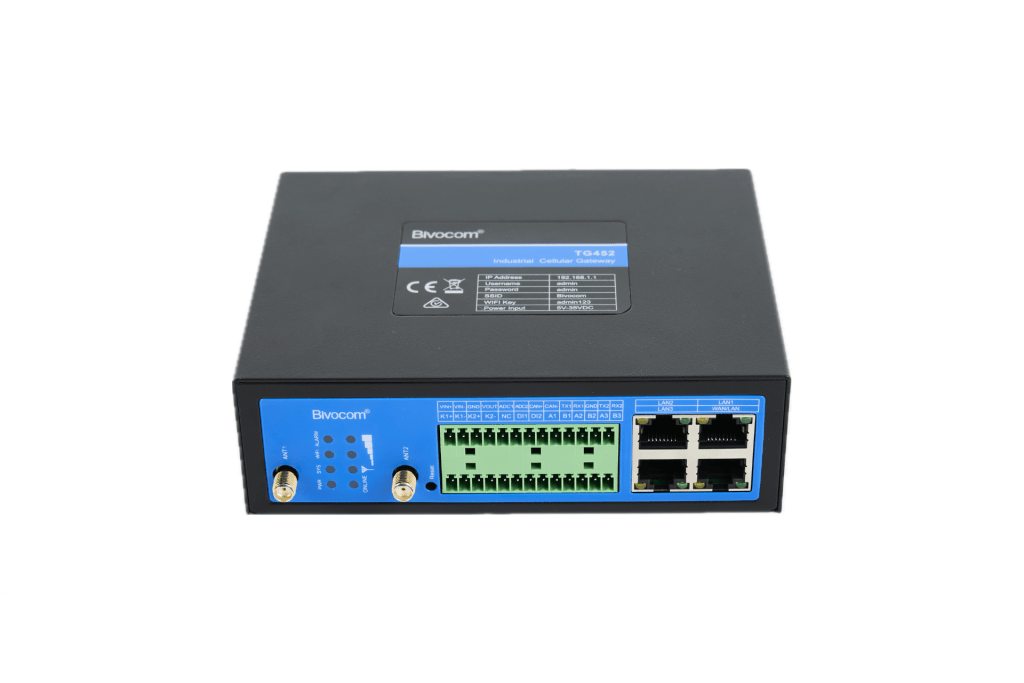
- Bivocom TG452 Industrial Gateway
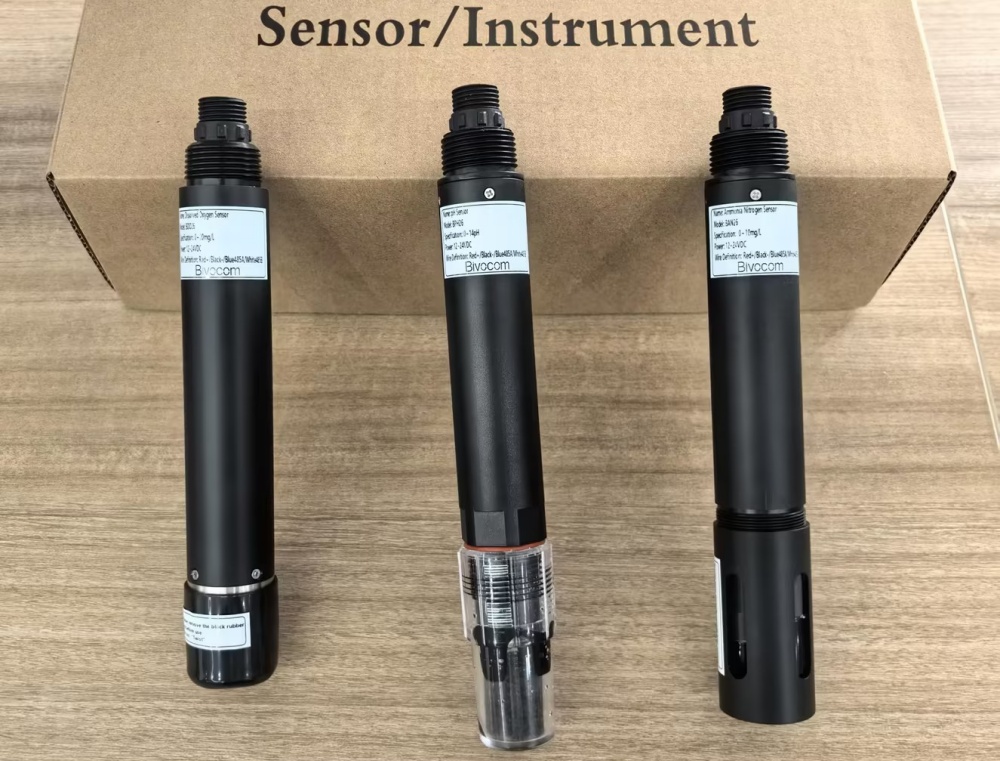
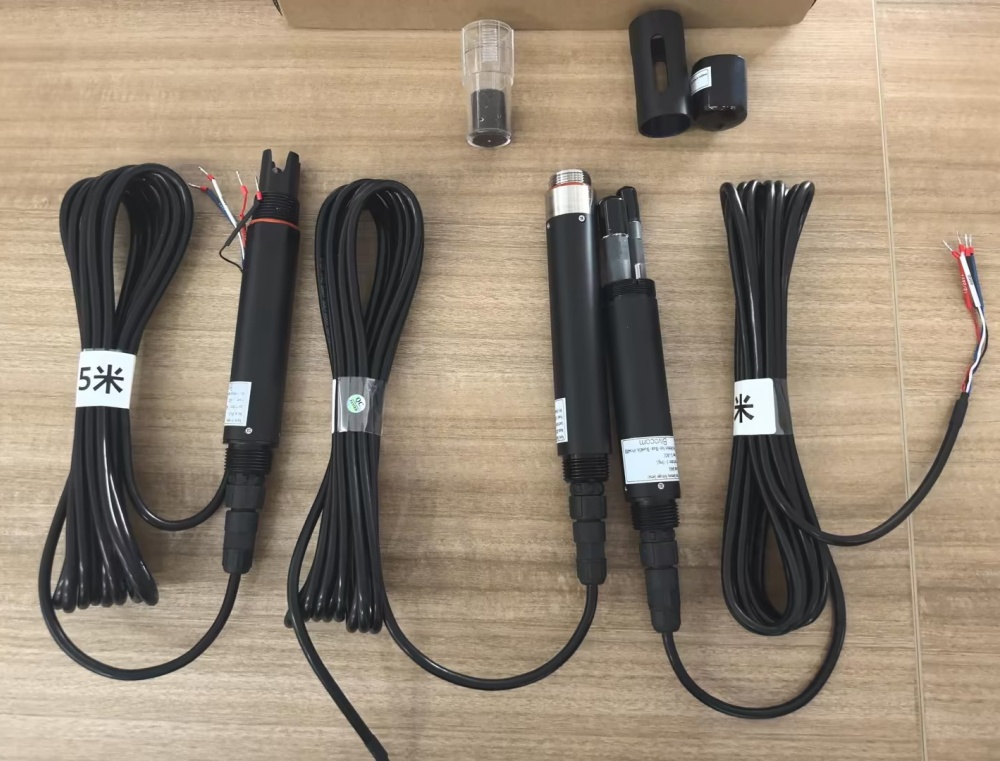
- Water Quality Sensors: Dissolved Oxygen, Ammonia Nitrogen, PH Sensor (with 3x 4-core twisted-pair shielded cable).
- Network Access: A computer on the same LAN as the gateway.
- Network Cable + Power Adapters
Step-by-Step Instructions
Step 1: Connect Sensors to the Gateway
First, establish a physical connection between your sensors and the gateway. All three sensors use a standard RS485 interface and the Modbus RTU protocol.
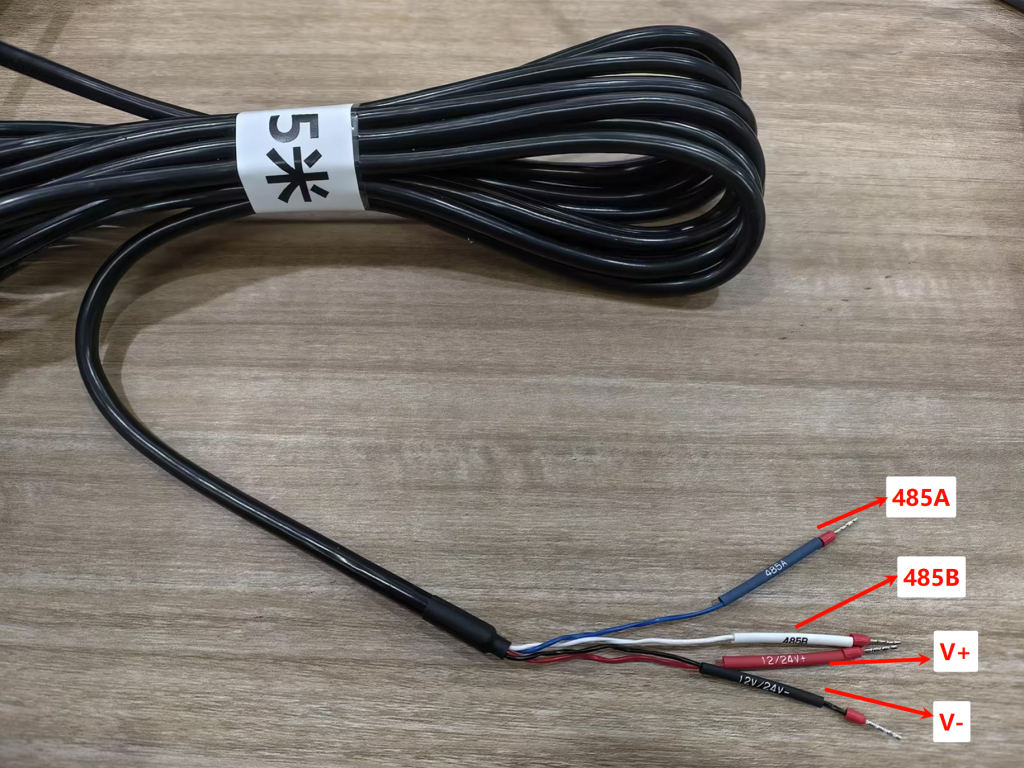
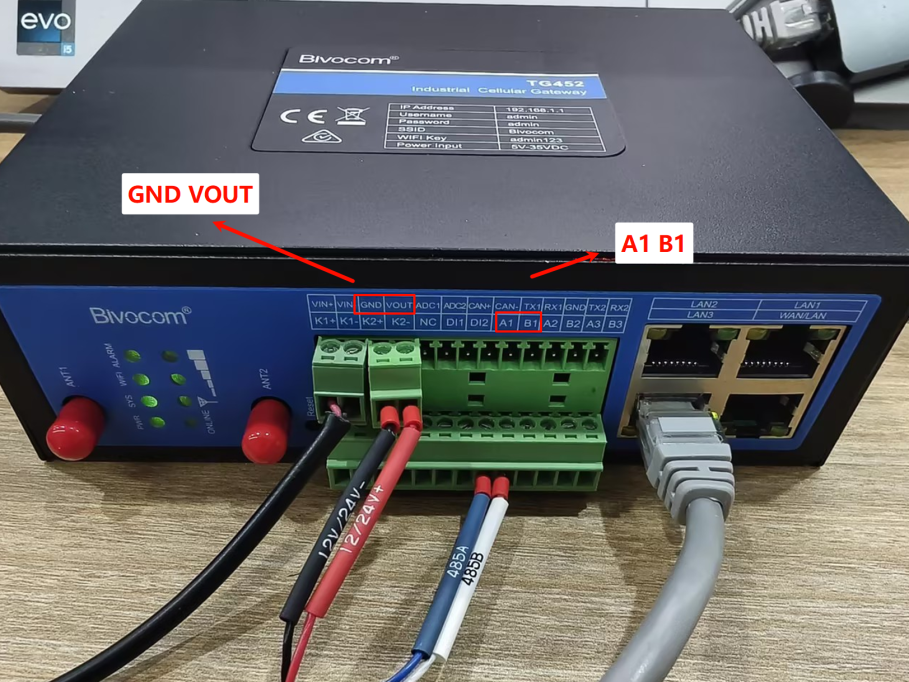
- Sensor Cable Definition: Use the TG452 to match sensor pins to the TG452’s RS485 ports (COM1/COM2/COM3). Red wire-power cord (12~24V), Black wire-ground wire (GND), Blue Line-485A, White Line-485B.
- Power Options: You can power the sensor directly from the gateway’s
VOUTandGNDterminals or use an external 12-24V power supply.
- Data Connection: Connect the sensor’s
AandBwires to a corresponding RS485 port on the gateway (e.g.,A1/B1for COM1).
Step 2: Enable Gateway Power Output
Log into the gateway’s WEBUI (typically at http://192.168.1.1). If you chose to power the sensor from the gateway, you must enable its voltage output.
- Navigate to Administrate > System.
- Find and enable the Output Voltage option.
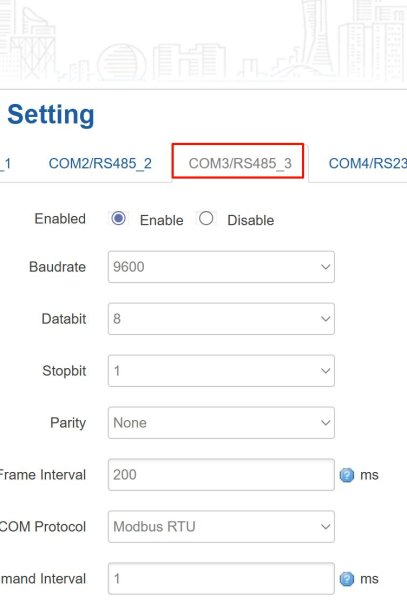
Step 3: Configure the Modbus Interface
For seamless data transmission, sensors and the gateway require consistent communication settings. Next, proceed to configure the communication port for each sensor accordingly.
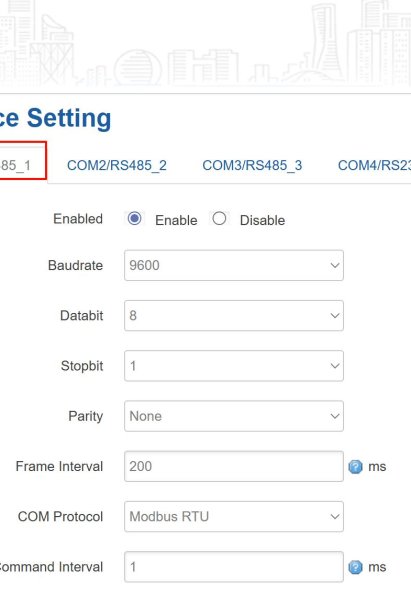
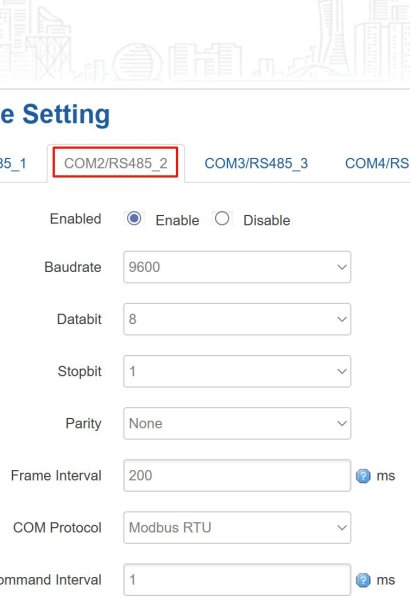
- Navigate to Data Collection > Interface Setting.
- Select the COM port you used (e.g., COM1).
- Configure it with these Modbus RTU parameters: Baud Rate: 9600, Data Bits: 8, Parity: None, Stop Bits: 1
Step 4: Add and Configure Modbus Rules
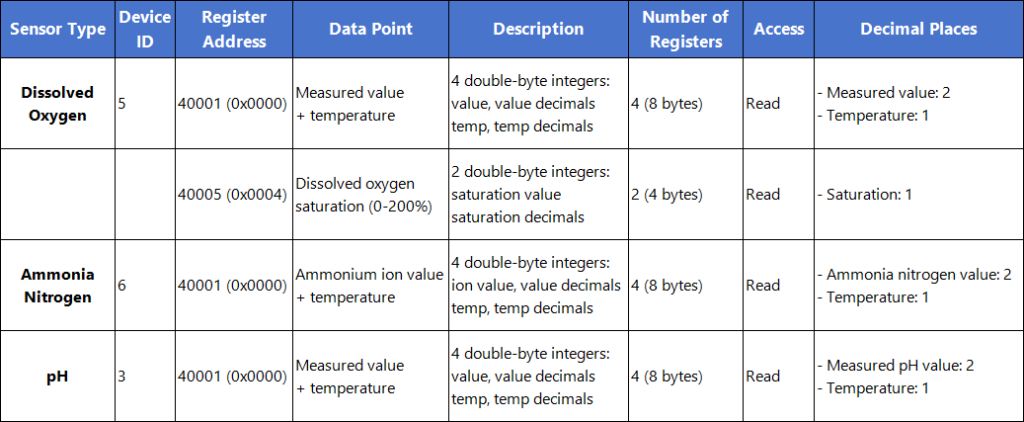
This step tells the gateway how to read data from each sensor—an essential part of the water quality sensor integration.
First, understand your sensor’s data structure. Each sensor provides measurements in blocks, as shown below. This tells you what data is available and where it lives.
Then, configure your gateway. Follow this straightforward process to build your setup:
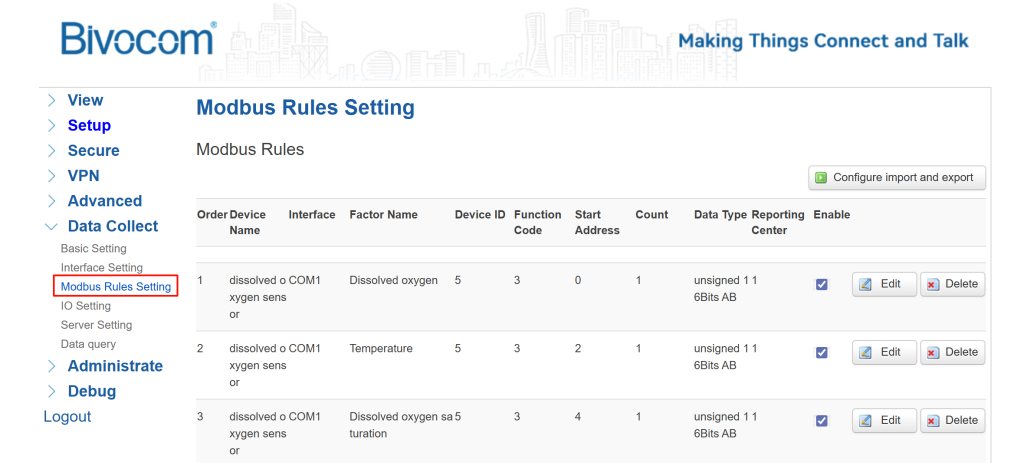
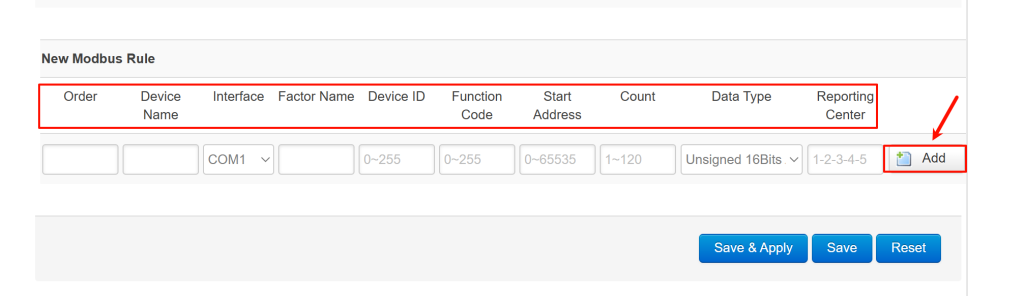
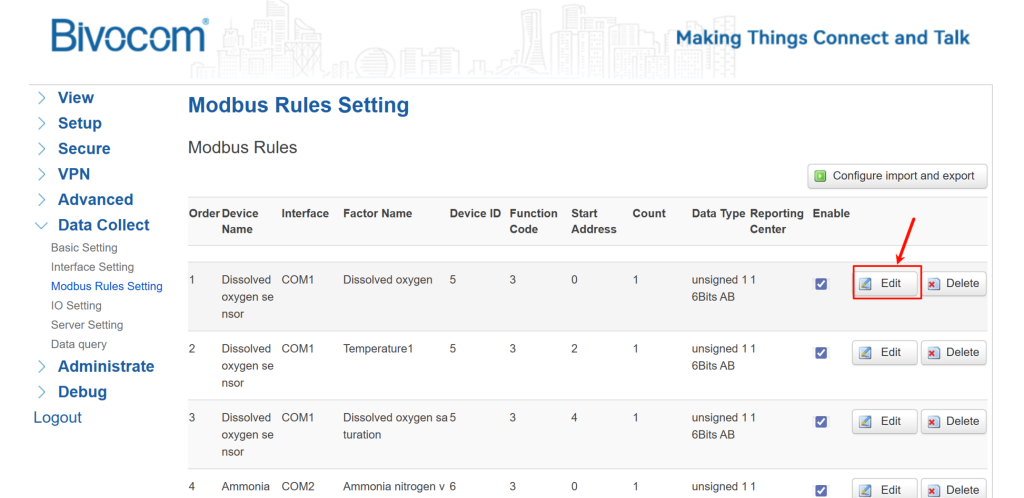
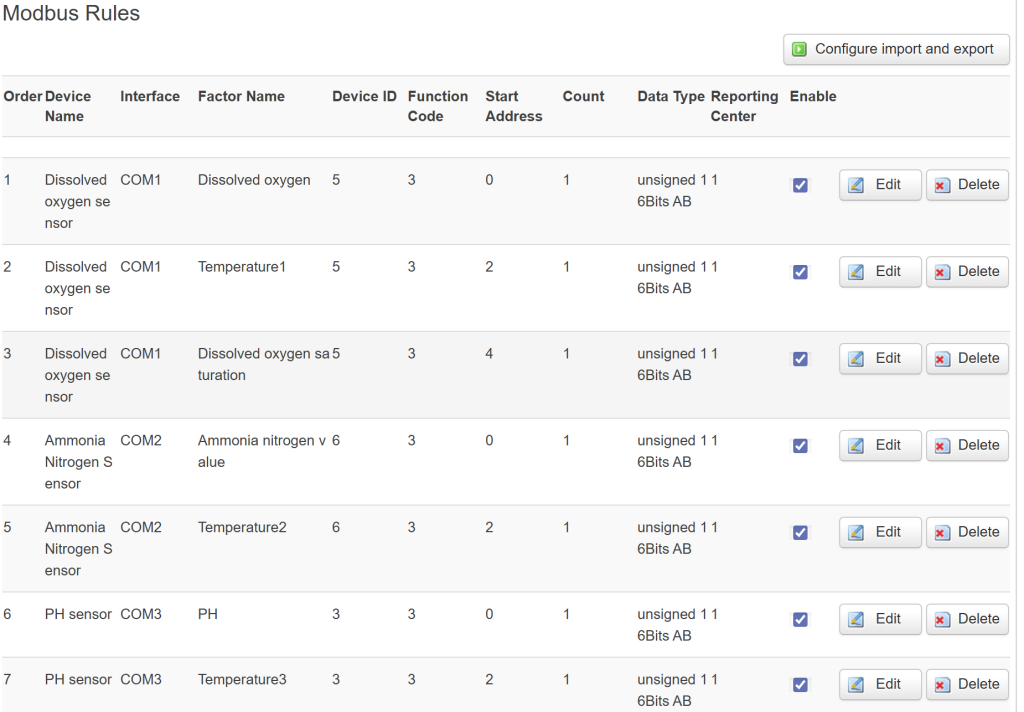
- Go to Data Collection > Modbus Rules Setting, and click “Add” to create a new rule for your first sensor.
- Complete the configuration details based on your specific sensor model, ensuring all values align with your sensor’s technical specifications.
- User-configurable fields: Order, Device Name, Factor Name (may be set as desired)
- Mandatory matched fields: Device ID, Function Code, Start Address, Count (must be configured to match the sensor’s parameters exactly)
- User-configurable fields: Order, Device Name, Factor Name (may be set as desired)
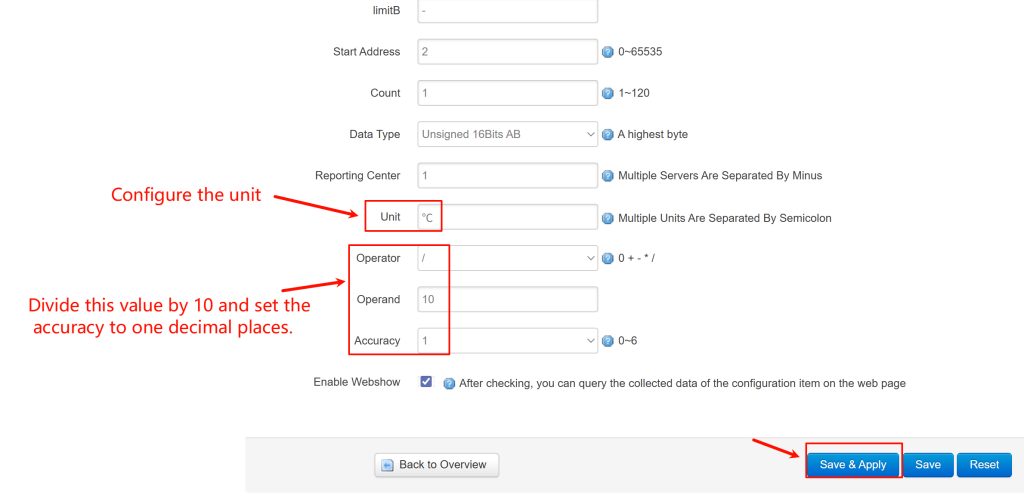
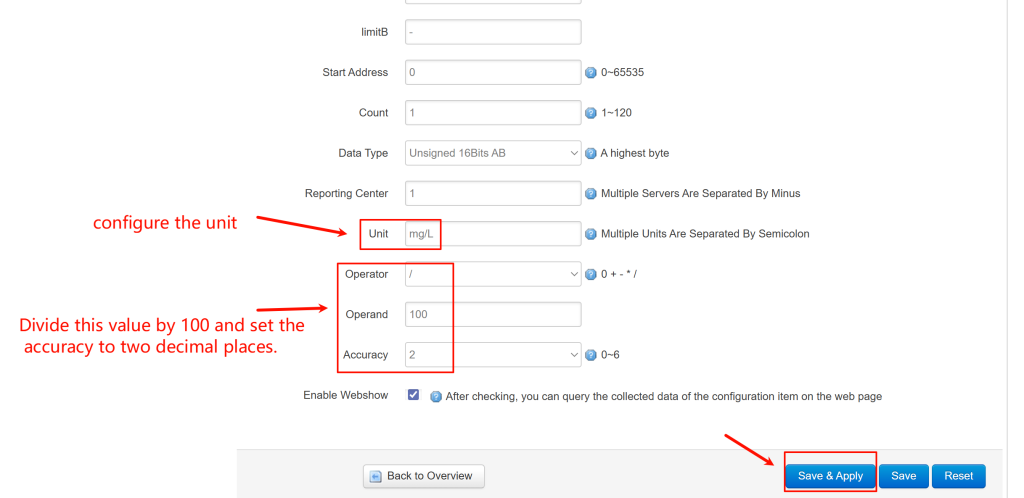
- Immediately configure its precision, click the “Edit” button (pencil icon) for the rule you just created. In the editing window, set the Decimal Places and Unit.
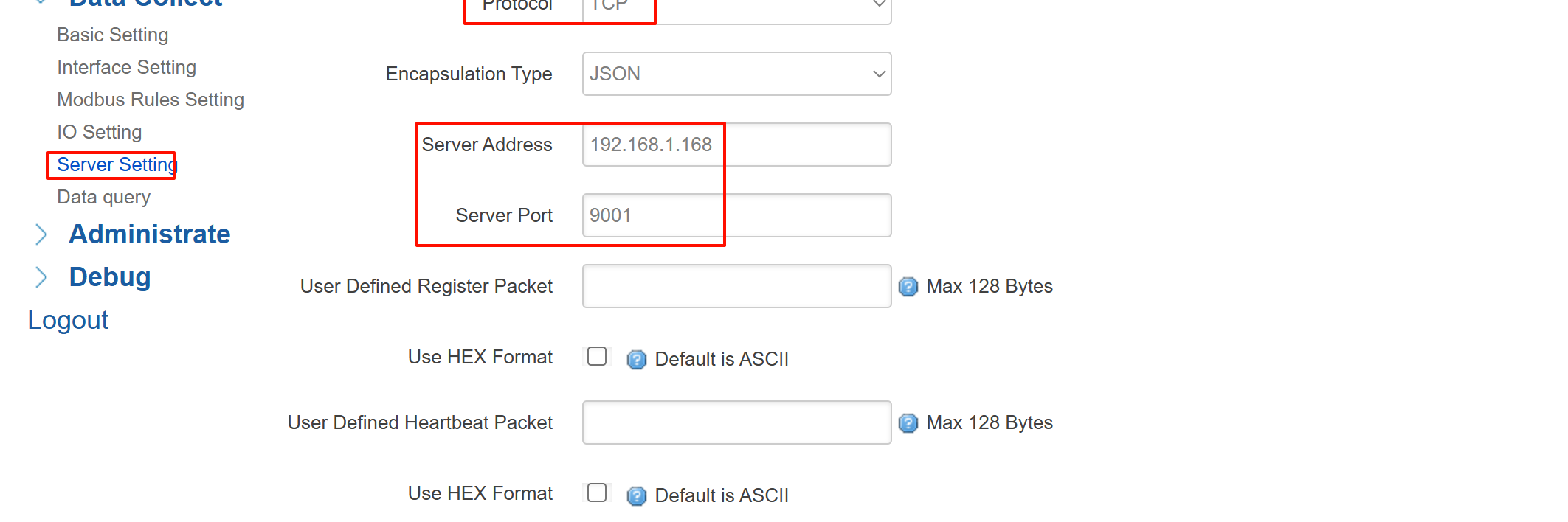
Step 5: Configure Data Reporting
To send your data to a monitoring platform or server.
- Go to Data Collection > Server Setting, and choose your preferred protocol (e.g., TCP).
- Enter the remote Server Address and Port.
- Set the reporting interval as needed.
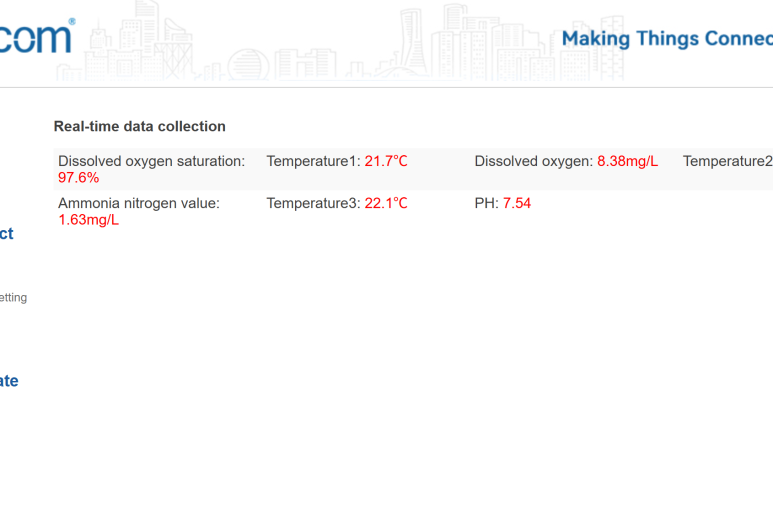
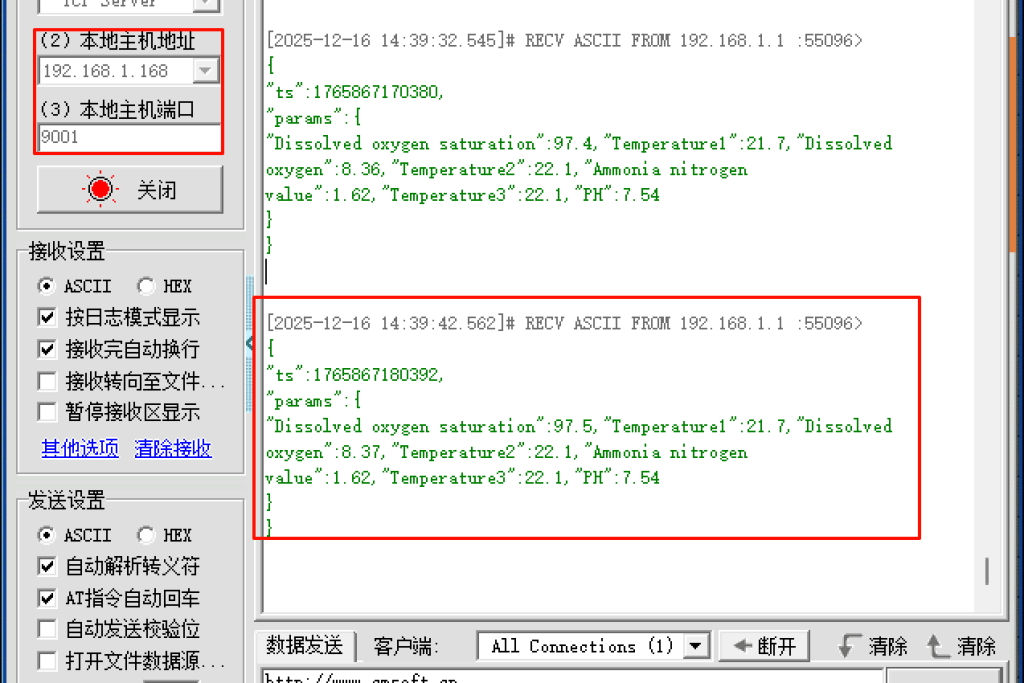
Step 6: Verify and Test
Finally, confirm your water quality sensor integration is working.
- Local Check: Go to Data Query in the WEBUI. You should see real-time values from your sensors.
- Server Check: Verify that your configured TCP (or other) server is receiving the data packets correctly.
Common Issues & Fixes
- No Data in WEBUI: Confirm cable connections and Modbus Device ID/Address settings. Ensure the correct COM port is enabled.
- Incorrect Values: Verify the decimal place and unit configuration for each factor.
- Data Not Reaching Server: Check the gateway’s network connection and the server’s firewall settings.




![[Case Study] Bivocom Smart Pole TG451 & Sensors](https://www.bivocom.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/09/Case-Study-Bivocom-Smart-Pole-TG451-Sensors-768x512.png)


Comment