LoRa (Long Range) and 4G LTE (Long-Term Evolution) are both used in the Internet of Things (IoT) space, but they cater to different requirements and use cases. Whether LoRa will replace 4G LTE in IoT depends on the specific needs of the IoT application. Here are some key considerations:
Range and Power Consumption:
LoRa: LoRa is known for its long-range capabilities and low power consumption. It is suitable for applications where devices are spread out over a wide area and need to communicate over long distances with minimal power usage.
4G LTE: LTE is designed for higher data rates and is well-suited for applications that require faster communication speeds. However, LTE may consume more power compared to LoRa.
Data Rate:
LoRa: Offers relatively low data rates suitable for applications with sporadic and small data transmission requirements, such as sensor readings and status updates.
4G LTE: Provides higher data rates, making it suitable for applications with more frequent and data-intensive communication needs.
Infrastructure and Cost:
LoRa: Typically has a lower infrastructure cost, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale deployments where devices are spread out over a wide area.
4G LTE: Requires more extensive infrastructure and may involve higher costs, but it offers faster and more reliable connectivity.
Application Requirements:
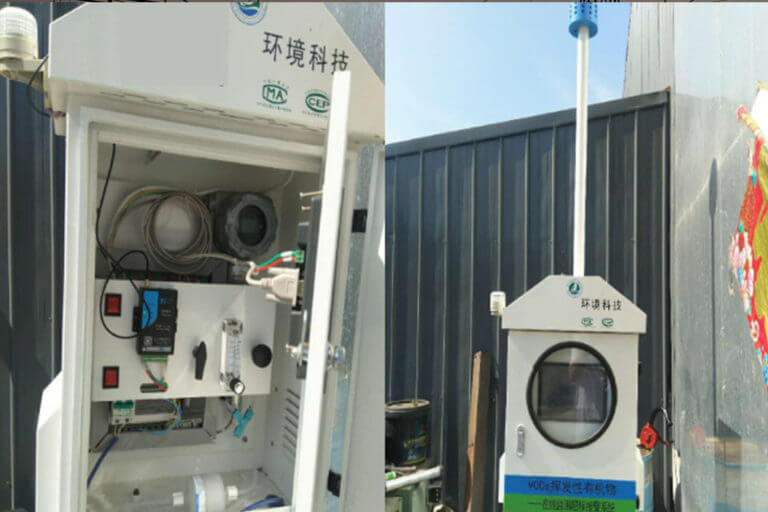
LoRa: Commonly used in scenarios like agriculture, smart cities, and industrial IoT where long-range communication and low power consumption are critical.
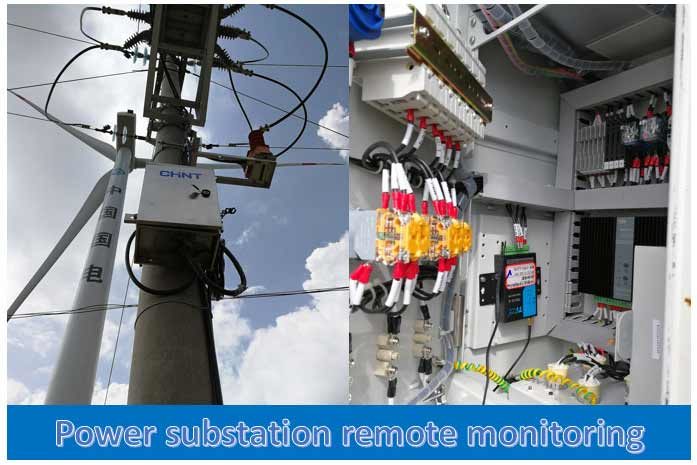
4G LTE: Preferred for applications requiring higher bandwidth, mobility support, and faster data transfer, such as connected vehicles or video surveillance.
Conclusions
In many cases, these technologies can complement each other within an IoT ecosystem. Hybrid solutions that leverage both LoRa for low-power, long-range communication and 4G LTE for higher bandwidth and mobility are not uncommon.
Ultimately, the choice between LoRa and 4G LTE in IoT depends on the specific needs and priorities of the application, including factors such as range, data rate, power consumption, and cost.



Comment